Bloomberg: Banks Can’t Afford to Ignore the $23 Trillion Market for Doing Good
They’re suddenly eager to offer incentives for social responsibility, writes Jacqueline Poh.
When British housing association London & Quadrant needed a 100 million-pound ($132 million) loan last year, its bank offered something unusually generous: A discount on interest if L&Q met an annual target of helping 600 unemployed residents find work.
Eight months later, L&Q, which builds and rents out affordable housing in London, is already more than 75 percent of the way there, putting it on course to unlock savings from its lender, BNP Paribas SA.
While it’s hard to imagine the world’s profit-driven banks offering incentives for doing good, corporate lending tied to some measurable sustainability metric—like cutting emissions or reducing food waste—surged eight-fold in 2018 to $36.4 billion, according to Bloomberg NEF.

There always seems to be a catch in finance, and while this time is no different, it may be more palatable. The fact is that people are now investing more than $23 trillion in socially responsible ways, according to the Global Sustainability Investment Alliance, and lenders can’t ignore them if they want to stay relevant.
“If this catches on, it is going to be the next big investment opportunity,” said Kajetan Czyż, the program director for sustainable finance at the University of Cambridge’s Institute for Sustainability Leadership. “Banks need to adapt to this new suite of opportunities this shift creates.”
In a few years, banks that fill their loan books with so-called positive-incentive deals could be better placed to not only attract clients, like sustainability conscious millennials, but also lower funding costs.
That’s because loans tied to what the industry refers to as ESG—environmental, social and governance—usually go to companies that have track records of profitability and debt repayment. L&Q, for one, has an A3 rating at Moody’s Investors Service and other borrowers like Belgian chemicals giant Solvay SA, French food company Danone SA, hotel operator Accor SA and Thames Water Ltd. are all investment grade.
“Sustainability topics are increasingly included in conversations with clients,” said Cecile Moitry, the Paris-based sustainable finance director at BNP Paribas, which was involved in at least 10 such deals last year according to data compiled by Bloomberg.
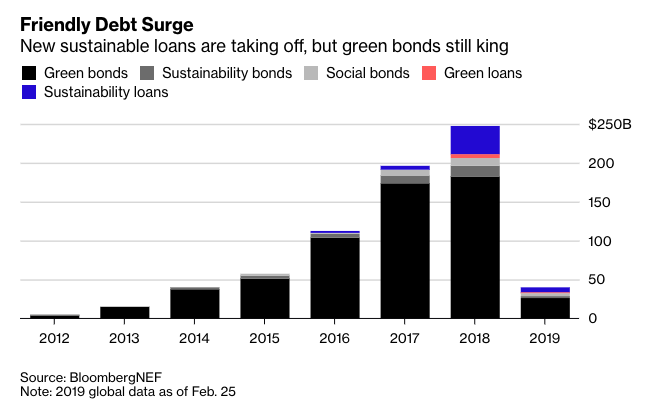
Up until now, banks have dabbled in "responsible banking" only symbolically. For more than a decade, they’ve arranged green bonds and green loans, used by companies to raise cash for environmental projects. But even last year’s $182 billion of green debt sales paled in comparison to over $6 trillion in global bond issuance.
That said, the new style of ESG lending that took off in 2018 could be a game changer, according to Dan Shurey, who leads Bloomberg NEF’s green and sustainable finance research. In just one year, these loans led the 26 percent increase in sustainable debt fundraising to a record $247 billion.
By allowing companies to use the cash raised for anything they want, ESG lending resolves one of the key issues preventing broader adoption of green bonds and greens loans. It’s the pricing of the facility, not the money itself, that’s tied to a socially responsible objective.
“An explicit price advantage was always the missing piece for green bonds,” said Shurey, who predicts volumes of ESG loans in 2019 will “vastly surpass” 2018. “Incentives for corporate borrowers are key for scaling the market.”
At the start, the interest rates on ESG loans look a lot like standard ones might. Then the rate changes depending on how well the company performs against its annual sustainability target. Meet the goal, interest rates drop. But miss the target, and they go up. Pricing details of these loans aren’t usually disclosed so it’s hard to gauge how big of an incentive they offer to companies.
Still, Xylem Inc., a U.S. maker of water equipment, said March 5 that it got an incentive of as much as 5 basis points on a $800 million revolving facility tied to a sustainability rating from Sustainalytics.
“This is a new world for most financiers and treasury teams”
Sustainable lending is still tiny in the grand scheme of finance, accounting for only 7 percent of the $507 billion of company loans in Europe last year. Its share is even smaller in $1.2 trillion U.S. corporate loan market, although some big deals—like the $3.5 billion ESG financing San Francisco-based warehouse developer Prologis Inc. signed in January—are putting ESG on the map.
There are hurdles to more mainstream adoption, such as the lack of agreement on how to objectively gauge a company’s social responsibility. While some loans are tied to a measurable metric, or key performance indicator (like CO2 emissions), others rely on ratings from one of more than a dozen agencies, including MSCI, Sustainalytics, RepRisk and the ISS Environmental & Social QualityScore.
Problem is, the scoring methods aren’t consistent. In July, U.S. think tank American Council for Capital Formation released a critical report after finding a correlation of 0.32 between the sustainability ratings of MSCI and Sustainalytics on companies in the S&P Global 1200 Index. By comparison, credit ratings of Moody’s and S&P Global Ratings are 0.90 aligned, it said.
“This is a new world for most financiers and treasury teams,” said Peter Elleman, the managing director for loan markets at ABN Amro NV in London, which is now lending in this space. He said having proof of a company’s social responsibility is a “a good indicator of good governance, and hence likely lower credit risk.”
Whether ESG lending ends up being a breakthrough in sustainable finance or a temporary fad, companies like the idea of extra cash. London utility Thames Water raised a 1.4 billion pound five-year loan in December tied to its Global Real Estate Sustainability Benchmark rating. Any interest savings will go to its charitable fund, which donates to causes related to water and the environment.
While L&Q wouldn’t say how much it expects to save when its five-year loan is repriced, its director of treasury, Martin Watts, called the discount “significant.” It needs to get at least 600 unemployed residents back into work in the first financial year, starting April, to unlock savings, with the goal rising by 25 in each subsequent year.
“It will make a material difference to our funding costs,” Watts said.
Source: Jacqueline Poh, Bloomberg
